
Established manufacturers and small or prototype developers prefer Vacuum Casting Service for precise and detailed production—for example medical device components, automotive parts, electronic casings, etc.
A silicon mold is created using the master model and the mixture of resins fills the vacuum mold. Then, cavities formed by the master model capture the details to shape the part before demolding. Meanwhile, the mold is reusable 10-50 times and consistently delivers a finely detailed surface with minimal porosity.
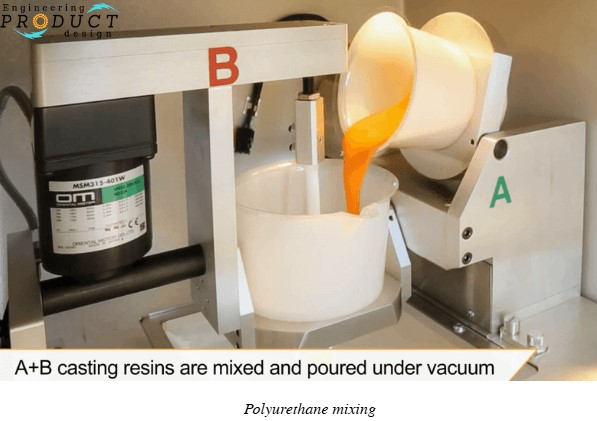

Typically, polyurethane and several other plastic and rubber-like resins can be used in the vacuum cast process to produce structurally tough and foam structures. In this article, we will elaborate on the vacuum casting advantages and disadvantages focusing on its process and applicability.
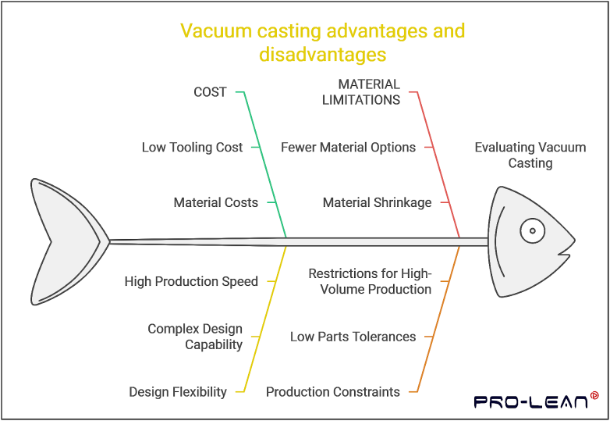
What are the Vacuum Casting Advantages?
In any new product design and improvement, manufacturers need to make prototypes first. They allow for testing of the functionality, design iteration, a showcase model, and detecting faults. Typically, injection molding and vacuum casting are the main options for this. However, injection molding costs are significantly higher due to extensive tooling requirements. Although vacuum molds are usable for a few production cycles, they cost approximately 10% of an aluminum or steel injection mold.

The list below elaborates on the key vacuum casting advantages in brief;
Low Tooling Cost
Unlike injection molding or another process, mold manufacturing does not require machining a mold with complex cavities. It is made by enclosing the master model ( replicate or desired item) with silicon molds, followed by model removal after creating the cavity. This significantly reduces the mold-making cost.
Design Flexibility
As mold making is not limited by the machine’s capabilities, like complex undercuts, deep channels, grooves, etc, the complex designs can be transferred using vacuum casting. You just need to have a master model, which can be cast or CNC-machined.
High Production Speed
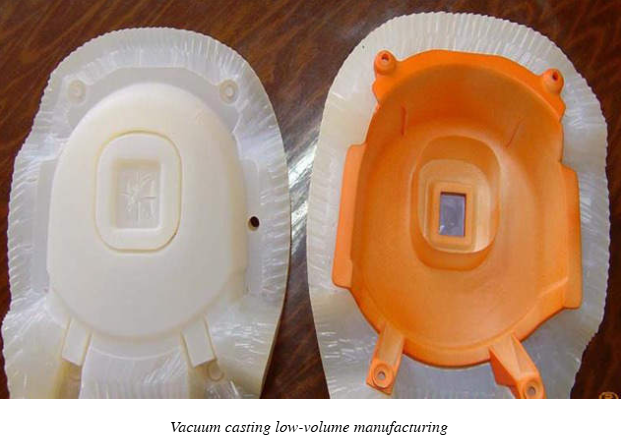

A typical project lead time for a vacuum cast project is about 5 to 10 days. Meanwhile, streamlined rapid prototyping services can convert your design into functional prototypes within 3 to 5 days, depending on the design complexity. It includes everything from replica model creation, mold making, production, finishing, and dispatching.
Fine Details and Low Surace Porosity
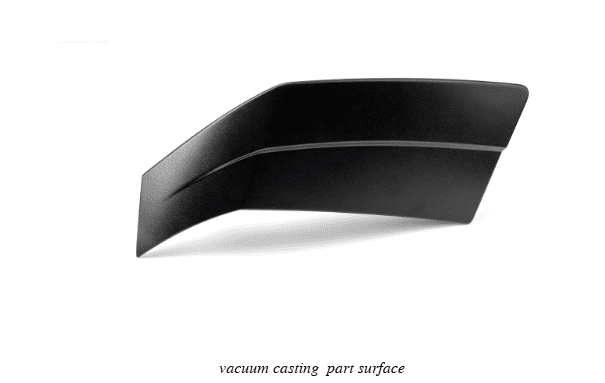
Since the vacuum casting process involves removing all the air from the silicone mold cavity before pouring the material, it eliminates the air and gas entrapment risk during the molding process. As a result, the material fully penetrates intricate mold features for a low porous and defect-free surface.
Material Costs
As mentioned previously, the vacuum casting method utilizes plastic-like resins instead of original raw plastic pallets. The plastic-like polyurethane resins are less costlier than the original pallets. However, they do not compromise the appearance and functional properties.
What are the Disadvantages of Vacuum Casting?
The vacuum casting process has some drawbacks too. Considering both vacuum casting advantages and disadvantages helps to avoid the mistakes that can cause product failure and optimize the benefits of this technology.
The disadvantages of vacuum casting are associated with surface finish quality, mold wear, and scalability.
Fewer Options for Material Selection
The type of material resins compatible with vacuum casting are fewer than injection molding and other processes. It mainly works with rubber and plastic materials, which are polyurethane resins prepared to mimic original properties. Some common options are ABS, PP, PC, and PA-like resins.
Material Shrinkage
The casting of large-sized parts tends to shrink during the cooling phase of the casting process. To avoid this, you need to consider the shrinkage rate and material volume during the primary material calculation.
Parts Tolerances
The vacuum casting parts tolerance typically ranges from ±0.5 mm to ±0.2 mm, which is lower than the general tolerance of injection molding processes(± 0.6 to 0.1mm) or CNC machining &±0.13 mm).
Restrictions for High-Volume Production
One of the main drawbacks of the vacuum casting process is its production volume capability. The silicone mold tends to wear after 10 or 15 cycles, affecting the part’s accuracy. An optimized mold can perfectly work up to 50 cycles, but not beyond that. You need multiple identical silicone molds for mass production, which is technically and economically not feasible in most cases.
When to Use it? Comparing Vacuum Casting Advantages and Disadvantages
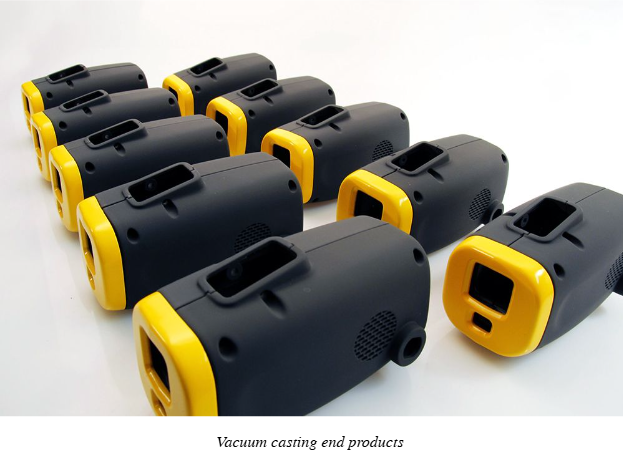

After discussing the vacuum casting advantages and disadvantages, we can say that it is not only about removing the air from the mold in a standard molding process, instead it is the process of creating precise prototypes and small-volume manufacturing. Different types of plastics alike polyurethane resins can be used for the vacuum casting process, which perfectly mimics the original properties.
- Low-cost rapid prototyping for design validation
- High-quality functional prototypes for automotive, aerospace, medical, electrical, etc.
- Small batch runs of complex designs
- The applications where surface porosity matters for performance and tight tolerances are less important.






